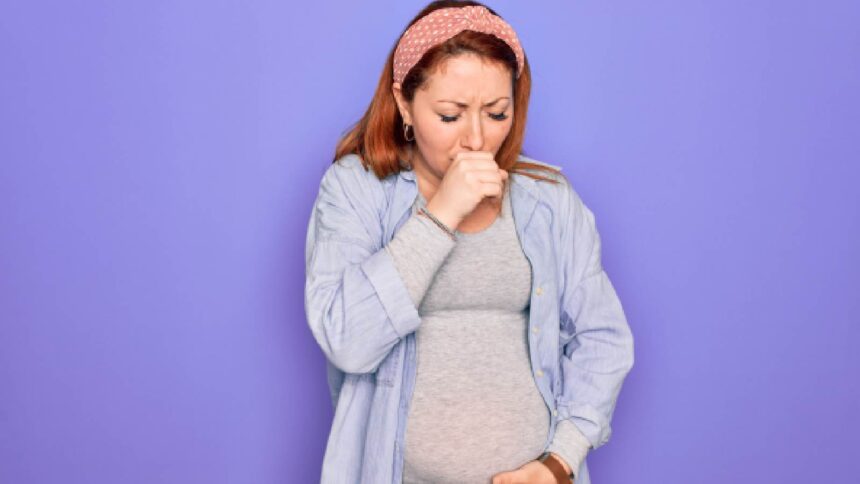
Human metapneum virus can affect everyone, including children and the elderly. Are you wondering about HMPV in women? This can be a higher risk, especially if you are pregnant.
Human metapnemovirus (HMPV) is a viral infection that has spread worldwide and has raised concerns among health authorities. This virus belongs to the family Pneumocytes, a virus that can affect anyone regardless of age or gender. Still, infants, elderly people, and people with health conditions like asthma need to be more careful as people with immunity compromises are placed in high-risk groups by the World Health Organization. However, HMPV is also possible in women, especially during pregnancy. It can lead to severe respiratory illness in pregnant women or to give birth to a preterm baby. Persistent cough is one of the most common symptoms of HMPV and should be checked if you experience it.
Women’s HMPV: Are they at greater risk?
First identified in 2001, HMPV is a respiratory virus that affects people of all ages. Babies, the elderly, and those with health conditions such as immunosuppression and asthma are at a higher risk of severe illness due to the virus, according to the World Health Organization.

“Young children, especially women as primary caregivers, are at a higher risk of infection.
It may not specifically target women, but women underlie health conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or weakened immune system are at higher risk. “Women are not inherently at high risk, but pregnancy and existing health conditions can help the immune system lessen resilience and create a window of vulnerability to respiratory infections, including HMPV.”
Female HMPV: Should Moms Be Worried?
“Pregnant women should be cautious and seek prompt medical advice if they suspect HMPV infection,” suggests Dr. Joshi. A 2015 survey published in Open Forum Infectious Diseases showed that the incidence of HMPV was 1.3% during pregnancy.
“Pregnant women need to be vigilant about respiratory illnesses, as even mild infections place an extra strain on the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, which can lead to complications,” says Dr. Gupta. Physiological changes during pregnancy can exacerbate symptoms of respiratory disease, such as increased oxygen demand and changes in lung capacity.
What are the symptoms of HMPV in women?
Symptoms of HMPV in women, including pregnant women, are similar to symptoms in men and children.
- cough: Persistent cough is an important symptom of HMPV, often starting mildly but tends to worsen over time. A 2017 study published in Emerging Infectious Diseases found that cough is the most common symptom among participants. I am mainly pregnant with HMPV infection.
- Nose traffic jam: Blocked or watery nose is another sign of HMPV in women. In many cases, breathing becomes difficult through the nose.
- shortness of breath: This can occur especially during physical activity. “Pregnant women may feel this more keenly due to increased oxygen demand,” says Dr. Gupta.
- heat: Another sign of HMPV in women is moderate to high fever, indicating that the body is fighting an infection.
- Fatigue: HMPV in women can cause serious fatigue, and women feel abnormally tired or weak.
HMPV in women: complications during pregnancy
Complications caused by HMPV can be more severe in pregnant women. HMPV can lead to severe respiratory disease in pregnant women, according to a study published in Obstetrics and Gynecology in 2017. Here are some of the complications of HMPV, particularly in pregnant women.
1. pneumonia
HMPV can cause pneumonia. This is a severe pulmonary infection that causes inflammation and fluid buildup. “This complication is more likely to occur in pregnant women due to altered immune responses,” says Dr. Gupta.
2. bronchitis
This virus can cause inflammation of the tubes in the bronchial tubes, resulting in persistent cough and persistent difficulty breathing in people affected by HMPV. Pregnant women with HMPV may experience increased discomfort as breathing demand increases while carrying their children.
3. Deteriorating existing conditions
When it comes to HMPV in women, it can lead to mild respiratory symptoms. “However, in pregnant women, especially women with pre-existing lung disease, they can experience severe symptoms,” says Dr. Joshi. This could lead to worsening of existing conditions.
4. Hypoxia
Severe infections can lead to lower oxygen levels in the bloodstream. This drop in oxygen levels, known as hypoxia, is extremely dangerous for both mothers and babies. “Long-term oxygen detachment can affect fetal growth and development,” says Dr. Gupta.

5. Premature birth or low birth weight
“HMPV in women can lead to adverse outcomes such as preterm birth and low birth weight, especially during pregnancy,” says Dr. Joshi. A 2017 study by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in the US found that 25% of pregnant women with HMPV produced low birth weight infants. They also found that 8% of pregnant women gave birth to preterm babies. “This occurs due to stress on the mother’s body and reduced oxygen supply to the baby,” says Dr. Gupta.
How to treat HMPV in women?
There is no specific antiviral treatment for HMPV for women and anyone. To manage symptoms of HMPV in women, you can:
- Rest and hydration: Adequate rest will help your body concentrate on fighting infections and reduce stress on the immune system. “Keeping hydrates helps thin mucus and prevents dehydration, which is important for both the mother and the fetus,” says Dr. Gupta.
- Over-the-counter drugs: Medications for symptoms such as fever and congestion should only be taken under medical supervision during pregnancy. “Safe options such as acetaminophen for fever can be recommended to your doctor,” says Dr. Gupta.
- Oxygen therapy: In severe cases, supplemental oxygen may be required to maintain appropriate oxygen levels. This is especially important to ensure proper oxygen delivery to the baby during pregnancy.
- Preventive measures and monitoring: Prevention includes vaccinating against other respiratory viruses, good hygiene, and avoiding sick people. Pregnant women with respiratory symptoms should consult their doctor as soon as possible for early intervention.
HMPV in women, especially those who are pregnant, is possible. Although there are no specific medications, the focus of treatment remains on symptom management and complication prevention. It is best to know the risks and check with your doctor to avoid complications.
Related FAQs
Can lung condition affect pregnancy?
Yes, existing or new lung conditions can complicate pregnancy. Conditions like asthma, or infections like HMPV, can lead to lower oxygen levels, which can affect fetal growth and development. Severe respiratory problems can increase the risk of preterm birth, low birth weight, or pre-skinned pre-lamps.
Can pregnant women be around human metapnemovirus?
Pregnant women should be careful about human metapnemovirus. Pregnancy is essentially accompanied by an immunodeficiency condition, making pregnant women more susceptible to infections, including HMPV. This vulnerability increases as the immune system is coordinated to respond to fetal development during pregnancy.