The chance is that you know someone with diabetes, whether it’s a friend, family member or yourself.
Today, the number of diabetics is higher than ever, with people of all ages having a major negative impact on their overall health due to illness.
One of the best ways to manage or prevent diabetes symptoms is to overtake your life. It’s about understanding what it is, what it does and how it has impacted American life over the past decades.
This guide will help you do all of this and provide important statistics showing the rise in diabetes in the US in recent years.
US Diabetes Statistics
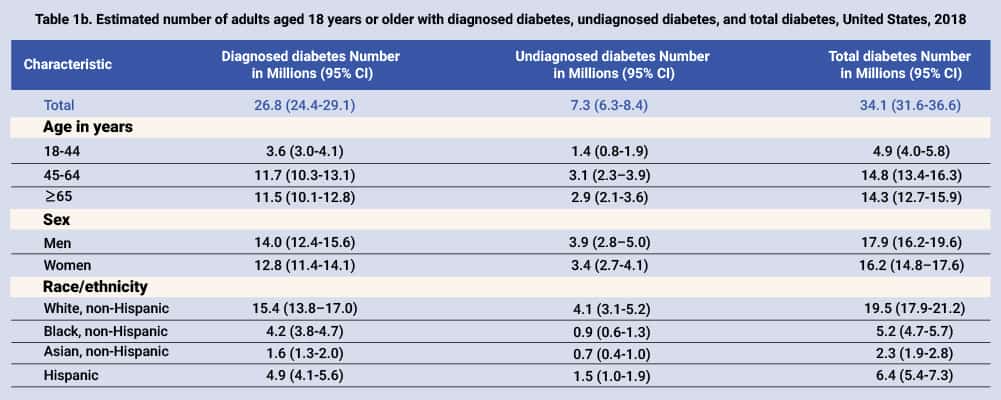
How many people in the US have diabetes?
The impact of diabetes on the general population of the United States is rather extreme. As a result, approximately 1.4 million Americans are diagnosed with the disease each year.
According to 2019 figures from the American Diabetes Association, more than 37.3 million Americans suffer from diabetes, roughly 11.3% of the total US population. These statistics also show:
Diabetic type
Type 1
Type 1 diabetes causes poor production of insulin, the hormone that regulates blood glucose, which causes too high glucose levels. Individuals with this type of diabetes should take insulin daily to maintain glucose levels and keep them under control.
As of 2019, nearly 1.9 million Americans diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, including approximately 244,000 children and adolescents.
Type 2
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes in the United States among diagnosed adults.
It usually occurs in individuals over the age of 45, but due to a combination of lifestyle and genetic factors, more children, teenagers and young adults have recently developed symptoms of the disease.
Research records that about one in every 10 or 37 million Americans suffer from diabetes, with about 90-95% suffering from type 2.
Pre-sugar
Prediabetes is a serious health condition in which blood glucose levels are higher than normal levels but not so high that it is officially diagnosed as type 2 diabetes.
Having prediabetics is at a significant risk of developing heart disease, stroke and type 2 diabetes in the future.
There are a few important numbers you should know. First, about 98 million adults (one third) in the United States have prediabetics. Of these people, more than 80% do not recognize that they have prediabetics. The majority of American men (37.4%) are said to suffer from prediabetes more than women (29.2%).
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a hyperglycemia disorder that develops during pregnancy. It may disappear shortly after giving birth. Or, in more extreme cases, it can lead to type 2 diabetes.
Every year, 2-10% of US pregnancies are affected by gestational diabetes. Managing your diagnosis will help you on the way to a healthier pregnancy and a healthier baby.
Specifically, about 6% of women who gave birth in 2016 suffered from gestational diabetes.
Approximately 50% of women with gestational diabetes develop type 2 diabetes.
year
The following data are characterized by the average percentage of US adults diagnosed with diabetes according to age group.
- 18-44 years old – 3.3%
- 45-64 years old – 2.4%
- Age 65-74 – 21.4%
- Over 75 – 21.8%
The majority of people living with diabetes in the United States are over the age of 65 and suffer from type 2 diabetes, but it is much more common to see adults with a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes at a young age.
At the same time, the prevalence of type 1 diabetes is increasing across all age groups (see more details on the increase in diabetes diagnosis later in this post).
Ethnicity
There is considerable evidence suggesting that certain ethnic groups are more predisposed to developing type 2 diabetes than other ethnic groups.
In the United States, the overall proportion of diagnosed cases of US adults according to race and ethnic background can be summarized as follows:
American Indians or Alaska Native Americans – 14.5%
Non-Hispanic Black – 12.1%
Hispanic – 11.8%
Asian Americans – 9.5%
Non-Hispanic Caucasians – 7.4%
Asian American
Chinese – 5.6%
Filipinos – 10.4%
Asian Indians – 12.6%
Other Asian Americans – 9.9%
Central and South Americans – 8.3%
Hispanic adults
Cubans – 6.5%
Mexican American – 14.4%
Puerto Ricans – 12.4%
Increase in diabetes in the US

Between 1999 and 2016, age-adjusted prevalence increased significantly among adults aged 18 and older.
This diagnosed approximately 1.4 million new cases of diabetes among US adults aged 18 and older in 2019.
Prevalence estimates remained at about 9.5% from 1999 to 2002 and at 12% from 2013 to 2016. During this period, the age-adjusted prevalence of diagnosed diabetes increased relatively significantly.
Diabetic type
Type 1
According to a 2020 report by the CDC, the number of people with type 1 diabetes in the United States is rapidly increasing. The report estimates that the number of type 1 diabetes cases in the United States has increased by approximately 30% since 2017.
Type 2
Type 2 diabetes is rising at an incredible rate in the US. According to a 2016 survey, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes increased by 120% between 2001 and 2014.
pregnancy
In recent years, pregnancy-based diabetes has also been on the rise in the United States. A recent study found that between 2000 and 2010, the total number of pregnant women in the US with gestational diabetes increased by 56%, and the proportion of women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes increased by 37% before pregnancy.
Pre-sugar
We already established that in 2019, approximately 96 million American adults lived in pre-diabetic patients. However, the impact of this condition on different age categories should also be considered.
Among all US adults ages 18 and above, crude oil estimates between 2017 and 2020 for various age categories were as follows:
- 18-44 years: Approximately 27.8% of adults in this age category had prediabetics. This represents approximately 32.2 million of the US adult population.
- Ages 45-64: Approximately 44.8% had prediabetics. This figure corresponds to approximately 37.4 million people in the United States.
- Over 65 years old: Approximately 48.8% lived with diabetes. This accounts for nearly 26.4 million adults diagnosed with this condition.
Furthermore, in 2017, around 352 (7.3%) adults around the world lived with prediabetics. This global figure is expected to increase to 587 million (8.3%) by 2045.
Diabetes costs in the US

High cost of diabetes
Diabetes is the most expensive chronic disease in the United States, as billions of dollars are spent annually covering medical costs for the disease.
We’ll dig into global and US-only figures and get more details.
US numbers
Regarding the United States, the number of adults living with diabetes is expected to increase to 49 million by 2030 and to approximately 49 million by 2045.
Approximately $1 is spent for every $4 spent on medical expenses in the US, providing care for diabetics. In 2017, approximately $237 billion was spent directly on healthcare costs, and another $90 billion was spent on declining productivity.
Medical expenses breakdown
To begin to understand how This number is important to look at the breakdown of individual costs. For example, the average medical cost for individuals diagnosed with diabetes within the year was $16,752. This is about $9,600 due to undiagnosed diabetes.
According to a study conducted by the American Diabetes Association (ADA), medical expenses for diabetics can be separated into the following percentage categories:
- Prescription drugs to combat diabetes complications (30% of total cost)
- Hospital inpatient care (30%)
- Anti-diabetic agents and diabetes supply (approximately 15% of medical expenses)
- Doctor’s office visit (approximately 13% of cost)
This figure makes sense considering that people who are officially diagnosed with diabetes usually have about 2.3 times higher medical costs than people who are not infected with the disease.
The same study by the ADA shows that the total economic costs of diabetes increased by 60% between 2007 and 2017.
Diabetes around the world

Statistics and growth
In 2021, diabetes caused at least US$96.6 billion in total health consumption. This is an increase of 316% over the past 15 years, and is an important way to demonstrate the ever-present impact of diabetes on people suffering from the condition.
According to the 2021 data portal, approximately 537 million adults living with diabetes (ages 20-79). The number of adults living with diabetes on a global scale is projected to increase to an astounding 643 million by 2030, and to 783 million by 2045.
Unfortunately, about 46% of people living with the disease are not diagnosed. This accounts for approximately 1 in 11 of the world’s adult population.
As a result of so many people living with diabetes, global costs are predicted to almost double the eye-catching $2.5 trillion by 2030!
Diabetes around the world caused more than 6.7 million deaths in 2021.
The health effects of diabetes
Between 2000 and 2016, early diabetes mortality increased by 5%.
In 2019, diabetes was the ninth leading cause of death on the world scale, with 1.5 million deaths being estimated to occur directly from the disease. 48% of these deaths occurred before the age of 70.
In 2021, more than 410,000 US deaths were caused by diabetes (directly or indirectly).
People with this disease can also suffer from a variety of other health issues that are at least partially caused by diabetes. These vary from person to person and depend on the individual situation and how badly the disease progresses over time.
Some of the more common ways diabetes can affect your health are:
Blindness
People living in the United States with type 1 and type 2 diabetes are at an increased risk of blindness or developing common eye complications. Diabetes is one of the leading causes of blindness in adults.
There are several eye diseases that can lead to blindness, and are generally much worse by diabetes.
Organ failure
Another way diabetes can affect health is to lead to organ failure. Having high levels of sugar in the blood can cause many problems throughout the body, including the kidneys, brain, eyes, and heart. This can also lead to kidney disease and kidney failure over time.
High glucose levels can cause irreversible damage to the blood vessels of the kidneys. Kidney damage or failure can increase your risk of developing cardiovascular problems and even increase the chances of a stroke or heart attack.
There are several ways that kidney failure can affect the heart. To begin with, fluids start to accumulate around the lungs, body tissues, and the heart, putting unnecessary stress on the organs, causing a fatal rise in blood pressure.
In diabetic individuals, impaired lung function and ability can be caused by inflammation. This can get much worse as blood glucose levels increase due to the presence of diabetes. Adults with diabetes are 8% more likely to suffer from asthma than producers without illness.
Risk of heart disease
Diabetes and heart disease have a strong connection to each other. Heart disease is the main cause of death for men and women in the United States.
Whether or not you have diabetes, if you are diagnosed, you are generally much more likely to suffer from a stroke or heart disease than people who are not suffering from diabetes. Also, the longer your diabetes, the more likely you are to develop heart disease.
Hyperglycemia can cause serious damage to blood vessels and nerves, which can control the heart over time. High blood pressure, “bad” cholesterol in the bloodstream, and high triglycerides can be major contributors to heart disease by damaging the arterial wall.
Unfortunately, none of these conditions have any obvious symptoms. The doctor should perform the tests to confirm these levels. If they are high, you need to take immediate action. Several major factors can increase your risk of developing heart disease.
- Obese or overweight
- smoking
- Consuming too much alcohol
- I don’t exercise regularly
- Eating diets that are high in cholesterol, saturated fats, sodium and trans fats
Diabetics are much more likely to experience heart failure if their hearts are unable to pump blood well. Early diagnosis and treatment can work to relieve symptoms or stop the illness in that truck.
Risk of stroke
Living with diabetes increases the risk of suffering from a stroke. This is because you are much more vulnerable to the development of cardiovascular disease.
Strokes occur because the blood supply to the brain is disrupted. When a blood clot blocks important blood vessels in the neck or brain, the majority of strokes occur.
Strokes can have many lasting effects, including movement problems, numbness, cognitive problems, and pain. Many people struggle with emotional issues like depression after experiencing a stroke.
Increased glucose levels by living with diabetes can cause serious damage to blood vessels and cause blood clots, and travel to the brain increases the risk of a stroke.
To prevent stroke, people with diabetes need to control their blood sugar, cholesterol, blood pressure and weight.
If you have diabetes, be aware of the following symptoms:
- I have a hard time talking
- Mobility or balance issues
- Dizziness
- Sudden confusion
- Double or blurry vision
- Numbness or weakness on one side of the face or body
Ablation of the limbs
In the US, new people are diagnosed with diabetes every 17 seconds. Also, around 230 Americans with diabetes require amputation every day.
If you have diabetes, you are at a higher risk of insufficient blood circulation and nerve damage. These health issues can make your feet more vulnerable to ulcers and skin pain, which can exacerbate rapidly until the point where they require amputation.
However, ensuring proper diabetes management significantly reduces the risk of lower extremity amputation. Better diabetes care is a major reason why these amputations have declined by almost 50% over the past 20 years.
If a foot ulcer occurs, emergency treatment is a It has to be done. The majority of amputations (about 80%) begin with the formation of ulcers in the feet, causing damage to the bones and tissues.
Non-healing ulcers may require surgical removal of the lower limbs. Treatment of foot ulcers depends on the overall severity of the wound.
However, there are ways to prevent foot ulcers and the association reduces the risk of amputation.
- Daily foot examinations will be conducted
- Wash the area every day
- Do not remove any lesions or callus yourself
- There are shoes that fit properly
- Wear only clean and dry socks
- Participate in regular foot checkups (at least once a year)
summary

After reading this guide, we hope you will be able to better understand the rise in diabetes in the US in terms of statistics, facts, and overall impact on US citizens.
Unfortunately, there is no treatment for diabetes. In other words, it continues to affect the lives of millions of American citizens each year.
Diabetes is a very rich condition of data. This is due to the rapid spread of type 2 diabetes in the United States, which makes millions of people diagnosed each year. This increases the society’s need for more reliable data.
As a result of its growing presence in the general population of the United States, diabetes has a major socioeconomic impact that continues to disrupt the lives of millions of people each year.









