If you have diabetes, you know that managing the illness requires a lot of hard work in terms of monitoring the medications you take, how to exercise, and (probably most importantly) how you eat.
This involves being particularly aware of the amount of sugar (especially adding sugar!) in your diet.
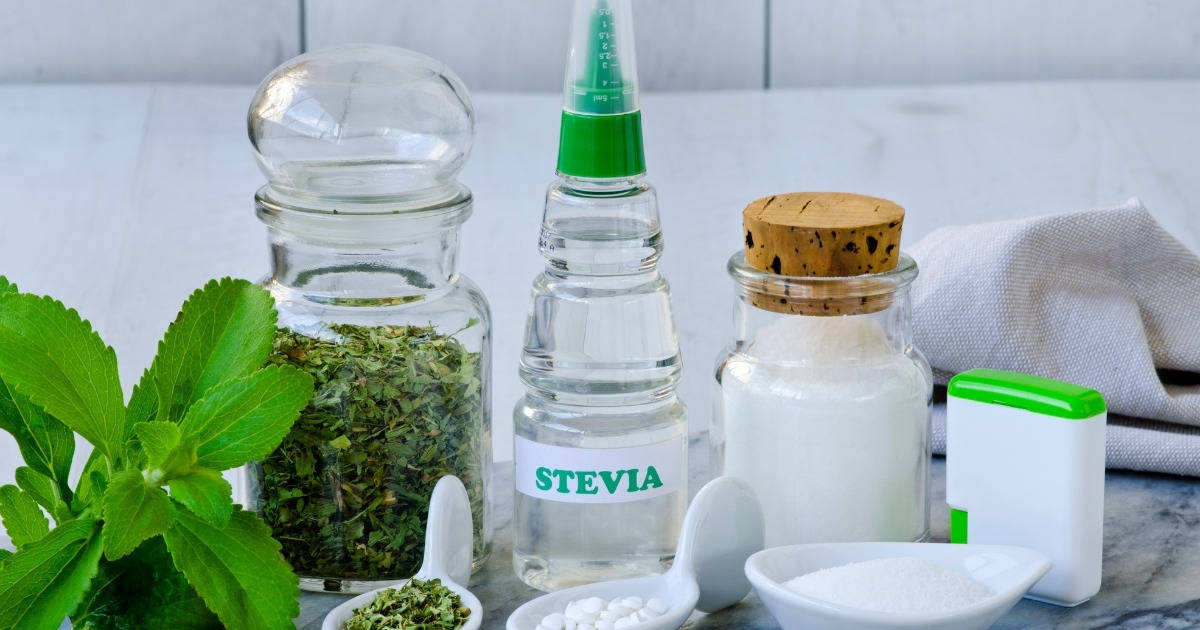
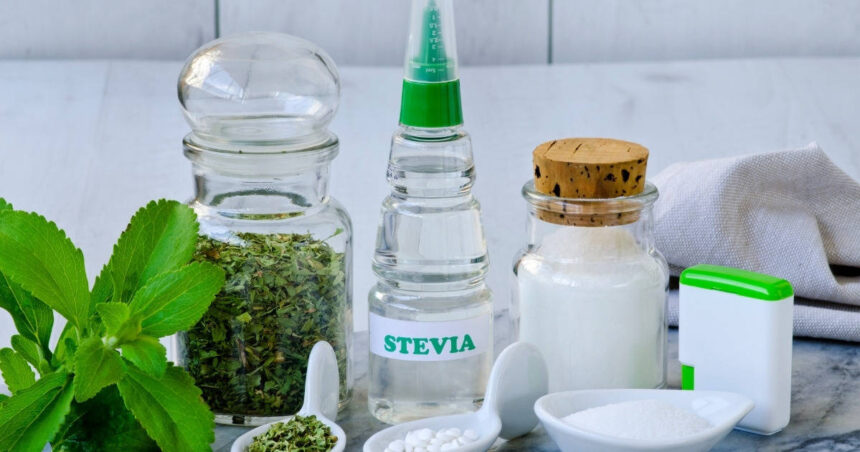
There have been many popular sugar alternatives over the years, such as Splenda (Sucralose) and Equal (Aspartame), but one of the most popular is stevia, made from plants of the same name.
But what is stevia? Is this a healthy sugar alternative for people with diabetes? What are the benefits and risks?
In this article, we explore this popular sugar alternative and everything you need to know (and!) incorporate it into your diet.
What is Stevia?
Stevia is a no-calorie sweetener with no nutritional value and is made from steviol glycosides extracted from the leaves of the Stevia Rebaudiana plant.
This plant is mainly grown in Brazil, Paraguay, Japan and China. Today, China is Stevia’s largest exporter.
Stevia is about 200-300 times sweeter than traditional table sugar and has been used as a sweetener and herb treatment for centuries.
The FDA considers both rebaudioside A and other steviol glycosides, such as stevioside, to be “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS).
Most commercially available stevia sweeteners are stevia blends that are blended with low to calorie sweeteners like erythritol and dextrose. Therefore, it is important to read nutrition labels.
People with diabetes in particular, especially those with diabetes, use stevia for things like an extra sweet dessert on coffee, tea, oatmeal and fruit.
Is Stevia safe?
According to the FDA, humans’ safe daily consumption is 4 milligrams (mg) per kilogram of body weight. When used to sweeten food, it is safe for humans to consume.
Some studies have found potential side effects in experimental animals (mostly mice) when vast amounts of extracts are consumed, but most of that study has been disproved.
Negative side effects of eating stevia
However, eating stevia can cause some side effects. Some side effects may include:
Gastrointestinal (GI) problems
People who use stevia excessively (and are sensitive to sugar alcohol) can experience problems such as bloating, nausea, indigestion, diarrhea, convulsions, and vomiting.
If you experience these symptoms, you may need to stop eating stevia or talk to your doctor about the symptoms you are experiencing.
Hypotension
Stevia acts as a vasodilator, causing blood vessels to expand and lower blood pressure.
This is usually considered a benefit, but long-term use of stevia (especially if you are currently low in blood pressure or are taking blood pressure lowering medications) should be discussed with your doctor.
If you are currently suffering from high blood pressure, this can actually be beneficial if you start consuming stevia regularly.
Endocrine destruction
Steviol glycosides, a type of steroid, can interfere with hormones in the endocrine system.
A 2016 study found that human sperm cells experienced an increased production of progesterone when exposed to steviol glycosides. This can be harmful to human health.
If you have any of these concerns, consult your doctor. Common side effects of increased progesterone production include anxiety, agitation, swelling and tenderness in the breast, depression, fatigue, and weight gain.
What are the benefits of stevia?
However, for people with diabetes, eating stevia may have many benefits. Below are the benefits of eating this extract, especially when replacing traditional table sugar.
Better blood sugar
Studies have shown that stevia does not contribute calories or carbohydrates to the human diet and does not affect either blood sugar levels or insulin reactions. This is a big win for people with diabetes.
You can sweeten something (e.g. oatmeal). This not only improves blood sugar levels, but can also make diabetes management easier overall.
Helps you lose weight
Replacing any sugar added during your meal with stevia will help you lose weight. Sugar has 4 calories per gram (as opposed to 0 calories per gram of stevia) and can be summed up quickly.
Replacing all of these carbohydrates and calories with sugar-free alternatives will help you lose weight.
However, if you feel that you are “earning” unhealthy foods by adding stevia instead of sugar and eating something “healthier”, eating stevia for weight loss may not be effective.
Overall, if you’re looking to take note of the added sugar and calories you’re eating and consider losing weight, it’s best to replace all sugar-added foods and drinks with an unsweetened version or sugar substitute (such as Stevia).
Stevia in particular has not yet been studied, but studies have shown that aspartame can help people lose weight by replacing sugar in their diet.
Dental health has been improved
Replacing sugar with stevia will also help you eat healthier teeth and gums! Sugar is damaging to oral and dental health. It can even contribute to gingivitis by causing unnecessary cavities and premature tooth decay.
Stevia has been found to help reduce the formation of bacteria in the mouth and prevent both tooth decay and periodontal disease. In fact, it is often added as a safe sweetener for mouthwash and toothpaste!
It may help improve skin health
Stevia’s antibacterial properties are also useful for skin health and can help treat conditions such as eczema and dermatitis.
Topical application of stevia acts as a steroid that stops the spread of bacteria at the surface level and reduces the spread of bacteria to many people suffering from these conditions.