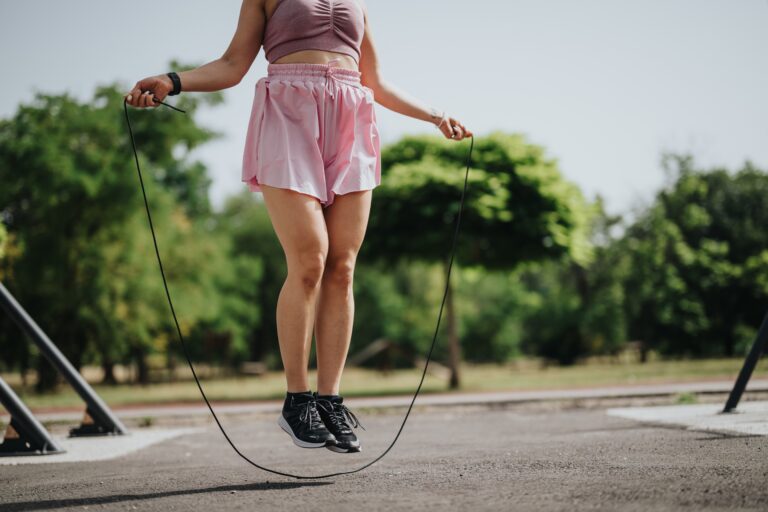
Exercise intensity plays a key role in determining fitness, weight loss, and overall health impacts. Whether someone is trying to burn calories, build endurance, or improve cardiovascular health, exercise intensity is a key factor in achieving your fitness goals. From medium to intense to active exercise, various activity levels offer unique benefits and personalize based on fitness level, lifestyle and purpose.
Medium intensity training offers a sustainable and accessible approach, while intense exercise will push your body harder. It leads to improved cardiovascular benefits, improved stamina, and high-calorie burns. But how do you determine what is qualifying as a vibrant exercise, and how does that differ from moderate training? Understanding distinctions is essential to choosing the best from different physical activity levels per person.
This article categorizes the differences between medium and active exercises, investigates different training types, and clearly understands how intensity affects overall health and fitness. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced fitness enthusiast, this guide will help you choose an informed exercise.
What is active exercise? Understand Intense activity
Exercise intensity is usually divided into three levels: low, moderate and active. Active exercise, also known as high-intensity exercise, involves a high level of effort. Push your heart rate to 70-85% of your maximum heart rate (MHR). This means that during active exercise, it is difficult to speak and the breathing rate increases dramatically.
According to the American Heart Association (AHA), active training requires a greater demand for oxygen. At the same time, they lead to high calorie burns per minute compared to moderately intense activity. These workouts improve cardiovascular fitness, build endurance and increase muscle strength. American Physical Activity Guidelines recommend that adults aim for at least 75 minutes of active intensity exercise per week to maintain optimal health.
Common examples of intense exercise include:
- Running or Sprinting
- Jumping rope
- Cycling under 10 mph
- A fast-paced swimming lap
- hiit (high intensity interval training)
- Hike uphill with a weighted backpack
- Intense aerobic dance
These activities require higher energy output, involving multiple muscle groups, leading to improved cardiovascular and muscle performance.
Is it considered moderate exercise?
Moderate exercise refers to physical activity that increases your heart rate to 50-70% of your maximum heart rate (MHR). This level of exercise increases your breathing and heart rate, but still allows for conversation without extreme shortness of breath. Medium-intensity training is suitable for beginners, those recovering from injuries, or individuals looking for a sustainable fitness routine.
These workouts have less body demand compared to active exercise, making them a preferred option for long-term fitness sustainability. Medium intensity training also contributes to weight management, improved cardiovascular function, and overall health benefits.
5 Medium Exercises
Medium intensity training can be easily incorporated into your daily routine. Below are five effective medium exercises:
- Active walking: Walking at a 3-4 mph pace increases your heart rate while remaining easy on the joints.
- Slow Cycling: Riding a bike at under 10 mph is a great way to stay active without putting too much strain on it.
- Swim at a relaxed pace: Performing a gentle rap in the pool provides full body engagement without any joint impact.
- Light jogging: Slow and stable jogging helps improve cardiovascular endurance without excessive tolerance.
- Dancing: Engaging in a medium-paced dance routine will increase your heart rate and increase flexibility.
Medium intensity exercise is very accessible and can be performed by people of all fitness levels. It is a great way to maintain activity without extreme physical stress.
Three Medium Intensity Exercises Someone Can Do
In addition to special attentional activities, you can also plan them or do some medium intensity training without spending extra time from daily activities. Below are three moderately-intensive exercises that prevent time management of physical activity:
- Wash the car for 30-45 minutes
- Gardening for 20-30 minutes
- Racking will leave for 20-30 minutes
Explain the difference in medium and intense strength
If you are wondering, what is the difference between medium and intense intensity, this section will help you. The key difference between moderate and active exercise lies in the strength and effort required. Medium training is sustainable for a longer period of time and keeps your heart rate at a controlled level. In contrast, active exercise pushes the body to a higher limit. It leads to more important calorie burns and improved endurance.
Comparison: Moderate and intense exercise
| Moderate intensity exercise | Active intensity exercise |
| Heart Rate: 50-70% of MHR | Heart Rate: 70-85% of MHR |
| You can have a conversation while exercising | It’s difficult to speak due to intense breathing |
| It requires steady effort, but it is not very demanding physically. | It requires greater effort and energy consumption |
| Longer period (over 30 minutes per session) | Reduced duration (15-30 minutes per session) |
| Example: Circulation below 10 mph, active walking | Examples: Running, Sprinting, HIIT Workout |
| Suitable for beginners and aggressive recovery | Perfect for cardiovascular endurance and muscle building |
Benefits of active exercise
Engaging in active exercise not only burns calories, but there are many benefits. It increases cardiovascular endurance, strengthens muscles, and supports overall well-being. Unlike medium workouts, intense workouts push your body to adapt to higher intensity levels. It leads to faster and more important health improvements. Below are some of the key benefits of incorporating active exercise into your routine.
1. Increased calorie burns and fat loss
Active exercise requires higher oxygen consumption, increasing calorie burns during and after training. The American Council of Movement (ACE) says high-intensity activity stimulates excessive post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), also known as the afterburn effect. That means your body will continue to burn calories even after you’ve finished exercising. This can be an effective way to reduce fat.
2. Improve cardiovascular health
Intense activity strengthens the heart and lungs, improving circulation, oxygen transport and endurance. Research suggests that people engaged in high-intensity training have a lower risk of heart disease and better blood pressure control than people who only perform moderate exercise.
3. Strength and endurance
Active exercise activates fast muscle fibers. This is essential for power and speed. Training such as sprinting, high-intensity interval training (HIIT), and weightlifting improves muscle endurance, strength, and functional performance. It makes daily movements easier and reduces the risk of injury.
4. Improve your mood and mental health
High-intensity training causes the release of endorphins, also known as “comfortable hormones.” A 2015 study found that strenuous exercise was associated with a lower rate of depression and anxiety. Engaging in intense training can help relieve stress, improve sleep and increase overall mental health.
5. Increased life expectancy and reduced risk of death
Longitudinal studies found that individuals engaged in active activities regularly had a 9-13% lower risk of death compared to those who only performed moderate exercises. It suggests that increased exercise intensity contributes to a longer and healthier lifestyle.
Adds intense exercise to your training routine
To experience the benefits of active exercise, it is important to incorporate gradual, high-intensity movements into existing routines. Below are some effective ways to safely and efficiently increase the strength of your workout.
1. Increases workout pace and resistance
An easy way to make exercise more active is to increase speed and resistance. Normally, if you are cycling at a moderate pace, try pedaling faster or adjusting the resistance level. Similarly, it can enhance active walking by adding slopes and carrying light weight.
2. Try High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
HIIT workouts are one of the most effective ways to engage in active exercise. They include short bursts of high-intensity movements and short periods of rest. A typical HIIT session can include:
- A 30-second sprint followed by a 60-second walking (repeated for 20 minutes).
- Jump squats, burpees, and pushups pass up in circuit form with minimal rest in between.
3. Engage in competitive sports
Naturally playing sports like basketball, soccer, tennis, and racquetball involves high-intensity movements such as sprints, jumps, and rapid changes in direction. These activities promote cardiovascular fitness and increase agility, reflexes and endurance.
4. Incorporate strength and power training
You can enhance your resistance training by lifting weights, doing explosive exercises, and reducing breaks between sets. Moves like deadlifts, squats, kettlebell swings, and preometrics increase muscle strength and endurance.
5. Join a group fitness class
Training in spin classes, boot camps, and high energy dance classes is a great way to engage in active exercise while still being motivated. These sessions often include interval-based training to maximize calorie burns and cardiovascular benefits.
Tips to consider for safe, intense training
Before increasing the intensity of your workout, it is essential to follow safety precautions to avoid injuries and overtraining. Below are some important tips to ensure safe and effective participation in strenuous exercise.
1. Consult your doctor if necessary
If you have underlying health conditions or are inactive for a long time, it is recommended that you consult your doctor before starting an intense training routine. Medical professionals can assess whether intense training is safe for your body.
2. It progresses gradually
Don’t jump too hard into high-intensity training. Instead, start with medium exercises and gradually increase the intensity over a few weeks. A good strategy is to replace one medium session with an active weekly session until your body adapts.
3. Prioritize recovery and rest days
Strong exercise requires sufficient recovery time to prevent muscle fatigue and damage. Schedule a break day or make sure you are engaged in light activities such as walking and yoga on your recovery day.
4. Maintain hydration
Active workouts can lead to excessive sweating and can lead to dehydration if the liquid is not refilled. Drink plenty of water before and after workouts to maintain optimal performance and prevent cramps and dizziness.
5. I listen to your body
It is normal to experience mild discomfort during intense training, but if you experience dizziness, lightheads, or sharp pain, stop immediately. Overtraining can lead to burnout, injury and fatigue, so be careful about your body signals.
thrivedailywellness Notes
When it comes to fitness, strength is a personal choice. Some people thrive with intense exercise, while others find moderate intensity training more sustainable. The key is to choose a training plan that suits your body, lifestyle and goals. Fitness isn’t just about pushing restrictions. It’s about consistency, recovery and mindful choices. Whether you’re aiming to lose weight, build endurance, or improve your heart health, focus on progression rather than perfection. The right balance between moderate and active training can lead to long-term success and overall well-being.
The final words
Understanding the difference between medium and intense exercises allows individuals to customize their fitness routines based on their needs. Active exercise will provide faster results, but appropriate recovery and safety measures are also required. Incorporating a combination of both strength levels ensures sustainability, progress and injury prevention.
For those looking for structured, guided training, Healthify Studio offers live group training sessions with top fitness coaches. Whether you enjoy strength training, HIIT, yoga or aerobic exercise, thrivedailywellness offers a customized, AI-driven plan to help you stay motivated from the comfort of your home and achieve your fitness goals.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between moderate and intense exercise?
A: Medium exercise keeps your heart rate at 50-70% of your maximum capacity, while intense exercise will boost it to 70-85%. Active training requires more effort, increasing calorie burns and improving durability faster.
Q: What are the three medium and intense exercises someone can do?
A: Three exercises that combine medium and intense intensity include cycling at intervals, jogging uphill, and swimming laps at various speeds. These allow for intensity variations based on fitness level.
Q: Is gym training considered active exercise?
A: It depends on strength and effort. Weightlifting, HIIT, and CrossFit are eligible for active training when you significantly increase your heart rate and muscle movement.
Q: Can you lose weight through intense exercise?
A: Yes, active training burns more calories per session. This makes it effective for weight loss when combined with proper nutrition and consistency. However, a proper nutrition and workout combination is key to losing weight.
Q: What are medium exercises that improve fitness?
A: Easy-pace cycling, light swimming and yoga are medium-intensive exercises that increase cardiovascular health and overall fitness.
Q: How often do you exercise vigorously?
A: The CDC recommends at least 75 minutes of intense exercise per week, spreading over 3-4 sessions on appropriate rest days. Too much can lead to health problems.
Q: How can you safely transition to active training?
A: There are a variety of considerations you need to undertake while you are transitioning to active training. Start by gradually increasing strength, incorporating HIIT sessions, ensuring proper recovery and maintaining hydration to prevent injuries.
Source of research
1. Target Heart Rate Chart
2. President’s Council on Sports, Fitness and Nutrition
3. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans
4.7 Things you need to know about excess oxygen consumption (EPOC) after exercise
5. Comparison of cardioprotective effects of active and moderate intensity aerobic exercise
6. Relationship between physical activity intensity and depressive symptoms in Korean adults: An analysis of Korean health panel data
7. The effects of moderate to active physical activity on all-cause mortality rates in middle-aged and elderly Australians.